Secret Scanning
Short, human version: this tool helps you find accidentally committed secrets in your code and configs — API keys, tokens, passwords, and similar items that shouldn't be in a repository.
What this is about
C# Dev Tools includes secret scanning powered by TruffleHog. It looks through project files, searches for high-entropy patterns and known signatures, and points out places that may contain sensitive data. Not every match is an actual secret — you may see false positives — but it's a reliable starting point for manual review.
What gets scanned
Common places we check:
- source files (C#, JavaScript, Python, etc.)
- configuration files (appsettings.json, web.config, etc.)
- environment files (.env, .env.local)
- documentation (README.md, docs folder)
- scripts (PowerShell, Bash, Batch)
Types of secrets that can be detected:
- API keys (AWS, Azure, Google Cloud, GitHub tokens, etc.)
- database credentials (connection strings, passwords)
- authentication tokens (JWT, OAuth secrets)
- encryption keys and private certificates
- third-party service tokens (Slack, Discord webhooks, etc.)
- custom patterns (you can add rules for project-specific secrets)
How it works (short)
- We discover files in the workspace matching supported types.
- Each file is analyzed using pattern matching, entropy checks, and TruffleHog rules.
- When suspicious items are found we try to verify them if possible.
- The tool generates a report with findings and metadata.
TruffleHog is an open-source engine that uses entropy analysis and many detection rules to reduce false positives and cover a wide range of secret types. You can also enable Git history scanning to find secrets that were committed in the past.
Scanning modes
- Filesystem Scan — a fast, lightweight scan of files in the current workspace. Good for quick checks.
- Git History Scan — scans commit history; more thorough but slower. Useful for audits.
How to start
- Open Solution Explorer
- Go to the Tools section
- Select "Secret Scanning"
- Pick a scan mode (Filesystem or Git History)
- Wait for the scan to finish
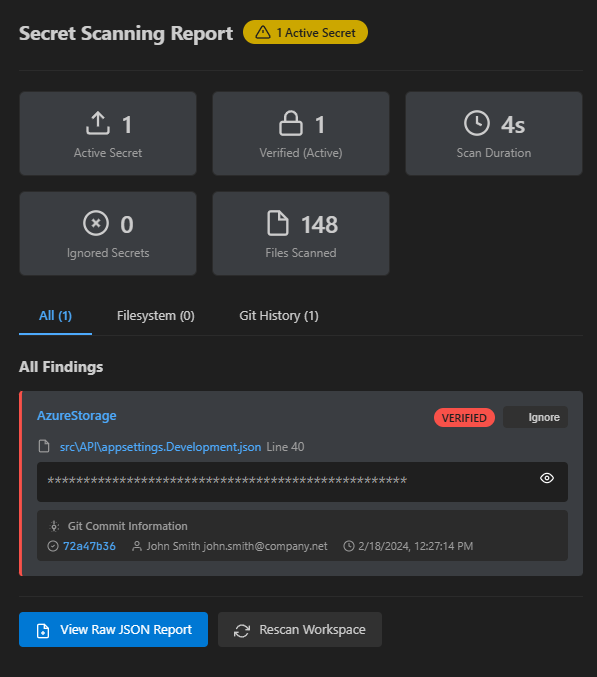
What the results include
- Active secrets — verified or high-confidence items that need quick action.
- All findings — the total list of potential secrets (both verified and unverified).
- File coverage — number of files scanned, duration and performance stats.
- Ignored — findings you've previously reviewed and marked as false positives.
Review and actions
For each finding you can:
- View details (file location and surrounding context)
- Open the file in the editor
- Mark as ignored (false positive)
- Copy details to your notes or ticketing system
Typical review flow:
- Check the context — is this actually a secret?
- If yes — rotate/regenerate the secret, remove it from code, and move it to a secret manager.
- If it's a false positive — mark it ignored.
What to do when you find a secret
- Rotate compromised keys and passwords immediately.
- Remove the secret from the repository and replace it with a safe configuration.
- If needed, inspect Git history and remove or rewrite past commits that contain secrets.
- Store secrets in a dedicated secret manager (Azure Key Vault, AWS Secrets Manager, etc.).
Simple best-practices (examples)
Don't hardcode secrets in code:
// BAD: secret in code
var apiKey = "sk-1234567890abcdef";
// BETTER: use environment variables
var apiKey = Environment.GetEnvironmentVariable("API_KEY");
Use "user secrets" during development:
dotnet user-secrets set "ConnectionStrings:DefaultConnection" "your-connection-string"
In production, keep secrets in a secure store (example: Azure Key Vault):
var client = new SecretClient(new Uri(keyVaultUrl), new DefaultAzureCredential());
var secret = await client.GetSecretAsync("database-connection");
Integrating into your workflow
- Run scans pre-commit (pre-commit hooks)
- Include secret scanning in CI/CD pipelines
- Schedule regular audits
- Train the team on secure handling of secrets
- Use a proper secret storage solution for production
Resources
- TruffleHog GitHub Repository
- TruffleHog Documentation
- OWASP Secret Management Guide
- Azure Key Vault Documentation
- AWS Secrets Manager
Regular secret scanning is an easy way to reduce the risk of accidental data leaks — the tool raises flags, and your team decides how to act on them.